# Kubernetes Role-Based Access Control(RBAC)
{% hint style="success" %}
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: (1) (1) (1).png) [**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)
[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte) (1) (1) (1).png) \
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
\
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  (1).png) [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**
[**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)** (1).png) ](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
Support HackTricks
* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
{% endhint %}
## Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Kubernetes has an **authorization module named Role-Based Access Control** ([**RBAC**](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/rbac/)) that helps to set utilization permissions to the API server.
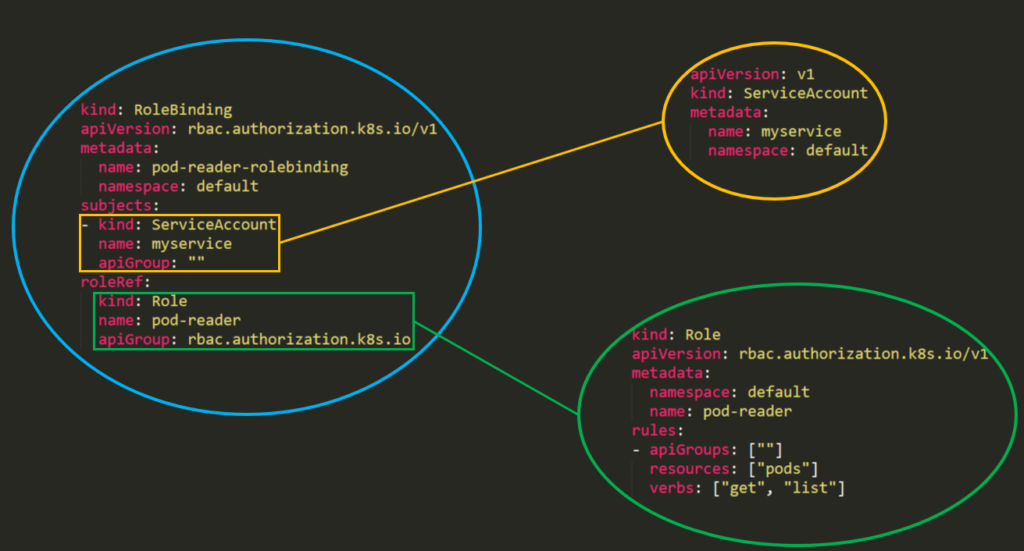
RBAC’s permission model is built from **three individual parts**:
1. **Role\ClusterRole –** The actual permission. It contains _**rules**_ that represent a set of permissions. Each rule contains [resources](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/#resource-types) and [verbs](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/authorization/#determine-the-request-verb). The verb is the action that will apply on the resource.
2. **Subject (User, Group or ServiceAccount) –** The object that will receive the permissions.
3. **RoleBinding\ClusterRoleBinding –** The connection between Role\ClusterRole and the subject.
The difference between “**Roles**” and “**ClusterRoles**” is just where the role will be applied – a “**Role**” will grant access to only **one** **specific** **namespace**, while a “**ClusterRole**” can be used in **all namespaces** in the cluster. Moreover, **ClusterRoles** can also grant access to:
* **cluster-scoped** resources (like nodes).
* **non-resource** endpoints (like /healthz).
* namespaced resources (like Pods), **across all namespaces**.
From **Kubernetes** 1.6 onwards, **RBAC** policies are **enabled by default**. But to enable RBAC you can use something like:
```
kube-apiserver --authorization-mode=Example,RBAC --other-options --more-options
```
## Templates
In the template of a **Role** or a **ClusterRole** you will need to indicate the **name of the role**, the **namespace** (in roles) and then the **apiGroups**, **resources** and **verbs** of the role:
* The **apiGroups** is an array that contains the different **API namespaces** that this rule applies to. For example, a Pod definition uses apiVersion: v1. _It can has values such as rbac.authorization.k8s.io or \[\*]_.
* The **resources** is an array that defines **which resources this rule applies to**. You can find all the resources with: `kubectl api-resources --namespaced=true`
* The **verbs** is an array that contains the **allowed verbs**. The verb in Kubernetes defines the **type of action** you need to apply to the resource. For example, the list verb is used against collections while "get" is used against a single resource.
### Rules Verbs
(_This info was taken from_ [_**the docs**_](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/authorization/#determine-the-request-verb))
| HTTP verb | request verb |
| --------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| POST | create |
| GET, HEAD | get (for individual resources), list (for collections, including full object content), watch (for watching an individual resource or collection of resources) |
| PUT | update |
| PATCH | patch |
| DELETE | delete (for individual resources), deletecollection (for collections) |
Kubernetes sometimes checks authorization for additional permissions using specialized verbs. For example:
* [PodSecurityPolicy](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/)
* `use` verb on `podsecuritypolicies` resources in the `policy` API group.
* [RBAC](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/rbac/#privilege-escalation-prevention-and-bootstrapping)
* `bind` and `escalate` verbs on `roles` and `clusterroles` resources in the `rbac.authorization.k8s.io` API group.
* [Authentication](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/authentication/)
* `impersonate` verb on `users`, `groups`, and `serviceaccounts` in the core API group, and the `userextras` in the `authentication.k8s.io` API group.
{% hint style="warning" %}
You can find **all the verbs that each resource support** executing `kubectl api-resources --sort-by name -o wide`
{% endhint %}
### Examples
{% code title="Role" %}
```yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: defaultGreen
name: pod-and-pod-logs-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods", "pods/log"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
```
{% endcode %}
{% code title="ClusterRole" %}
```yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
# "namespace" omitted since ClusterRoles are not namespaced
name: secret-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
```
{% endcode %}
For example you can use a **ClusterRole** to allow a particular user to run:
```
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
```
### **RoleBinding and ClusterRoleBinding**
[**From the docs:**](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/rbac/#rolebinding-and-clusterrolebinding) A **role binding grants the permissions defined in a role to a user or set of users**. It holds a list of subjects (users, groups, or service accounts), and a reference to the role being granted. A **RoleBinding** grants permissions within a specific **namespace** whereas a **ClusterRoleBinding** grants that access **cluster-wide**.
{% code title="" %}
```yaml
piVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
# This role binding allows "jane" to read pods in the "default" namespace.
# You need to already have a Role named "pod-reader" in that namespace.
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: default
subjects:
# You can specify more than one "subject"
- kind: User
name: jane # "name" is case sensitive
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
# "roleRef" specifies the binding to a Role / ClusterRole
kind: Role #this must be Role or ClusterRole
name: pod-reader # this must match the name of the Role or ClusterRole you wish to bind to
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
```
{% endcode %}
{% code title="ClusterRoleBinding" %}
```yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
# This cluster role binding allows anyone in the "manager" group to read secrets in any namespace.
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: read-secrets-global
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: manager # Name is case sensitive
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: secret-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
```
{% endcode %}
**Permissions are additive** so if you have a clusterRole with “list” and “delete” secrets you can add it with a Role with “get”. So be aware and test always your roles and permissions and **specify what is ALLOWED, because everything is DENIED by default.**
## **Enumerating RBAC**
```bash
# Get current privileges
kubectl auth can-i --list
# use `--as=system:serviceaccount::` to impersonate a service account
# List Cluster Roles
kubectl get clusterroles
kubectl describe clusterroles
# List Cluster Roles Bindings
kubectl get clusterrolebindings
kubectl describe clusterrolebindings
# List Roles
kubectl get roles
kubectl describe roles
# List Roles Bindings
kubectl get rolebindings
kubectl describe rolebindings
```
### Abuse Role/ClusterRoles for Privilege Escalation
{% content-ref url="abusing-roles-clusterroles-in-kubernetes/" %}
[abusing-roles-clusterroles-in-kubernetes](abusing-roles-clusterroles-in-kubernetes/)
{% endcontent-ref %}
{% hint style="success" %}
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: (1) (1) (1).png) [**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)
[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte) (1) (1) (1).png) \
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
\
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  (1).png) [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**
[**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)** (1).png) ](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
Support HackTricks
* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
{% endhint %}
 (1) (1) (1).png) [**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)
[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte) (1) (1) (1).png) \
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
\
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  (1).png) [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**
[**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)** (1).png) ](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
 (1) (1) (1).png) [**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)
[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte) (1) (1) (1).png) \
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
\
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  (1).png) [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**
[**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)** (1).png) ](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
 (1) (1) (1).png) [**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)
[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte) (1) (1) (1).png) \
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:
\
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  (1).png) [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**
[**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)** (1).png) ](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)